Why Is My CPU Overclocking Itself? – All You Need To Know
As a dedicated PC builder, you may have experienced the perplexing situation of your CPU seemingly overclocking itself without manual intervention. This occurrence can be puzzling and cause concern for users who value stability and control over their system’s performance.
Your CPU may overclock itself due to automatic boosting technologies (e.g., Intel Turbo Boost), aggressive motherboard default settings, faulty motherboard voltage regulation, thermal throttling, or conflicts with software utilities.
This comprehensive guide will explore the reasons behind self-overclocking CPUs and provide a step-by-step approach to troubleshoot and resolve this unexpected behavior.
Understanding CPU Overclocking:
Before delving into the reasons for self-overclocking, it’s crucial to grasp the concept of CPU overclocking itself. Overclocking involves pushing a CPU’s clock speed beyond its manufacturer-specified limits to achieve higher performance.
The two critical speeds set by manufacturers are the base clock, representing the minimum guaranteed speed, and the boost/turbo clock, indicating the maximum speed achievable under increased workload demand.
What Triggers Automatic CPU Overclocking?

Automatic CPU Boosting Technologies:
Modern CPUs from Intel or AMD come equipped with automatic boosting or overclocking technologies. Examples include Intel Turbo Boost and AMD Precision Boost.
These technologies dynamically increase the CPU’s clock speed within set limits based on workload demand and temperature.
If you observe your CPU clock speed surpassing the base or boost clock, these technologies likely work automatically to enhance performance without manual intervention.
Aggressive Default BIOS Settings:
The BIOS (Basic Input/Output System) is critical in initializing components like the CPU during boot and contains settings that govern their functioning.
Some motherboard manufacturers ship products with aggressive auto-overclocking rules enabled in the default BIOS options.
This can lead to higher-than-expected CPU speeds without user consent. Checking and adjusting these settings in the BIOS can rectify this issue.
Faulty Motherboard Overvolting CPU:
In rare cases, a defective motherboard may supply excessive voltage to the CPU, forcing it to operate at abnormally high clock speeds.
Motherboards regulate power and voltage delivery to the CPU, and a malfunction can result in unintentional overclocking.
A motherboard replacement might be necessary if other potential causes are ruled out.
Thermal Throttling And Speed Fluctuations:
When a CPU overheats beyond safe limits, thermal throttling mechanisms kick in to reduce power consumption and heat generation.
This can make the CPU downclock itself temporarily, creating the appearance of sudden overclocking once temperatures normalize.
Checking the CPU cooler installation, thermal paste application, and addressing dust buildup can help resolve thermal issues.
Unstable Power Delivery To CPU:
The power supply unit (PSU) is responsible for providing clean and stable power to the CPU. If the PSU fails to deliver a consistent voltage, the CPU may behave erratically and appear to overclock itself.
Before suspecting the PSU, it’s essential to rule out software issues and consider swapping in a different PSU for troubleshooting.
Conflicts Between Software Utilities:
Various software-related scenarios can lead to the CPU incorrectly appearing to overclock itself.
Multiple system monitoring utilities polling CPU clock speeds simultaneously, background programs consuming significant CPU resources, or conflicts with overclocking utilities can result in misleading readings.
Uninstalling unnecessary applications, updating drivers, and resetting Windows power options can help eliminate these software-related conflicts.
Read More: Bad CPU Type In Executable Homebrew | How To Fix The Error
How To Confirm If Your CPU Is Truly Overclocked?
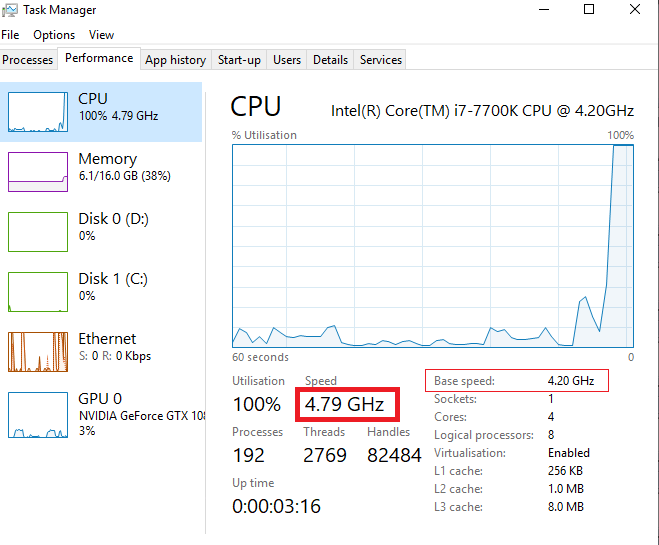
Before attempting to resolve the issue, confirming whether your CPU is genuinely overclocking is crucial. Utilize monitoring utilities like Task Manager, CPU-Z, HWiNFO, and Core Temp to check CPU clock speeds under idle and load conditions. Cross-verify readings between multiple programs to ensure accuracy.
Resolving Unwanted CPU Overclocking:
If your CPU is indeed overclocking itself, follow these troubleshooting steps:
Enter BIOS and Reset to Default:
- Access the BIOS during boot (typically using the DEL key).
- Load “Optimized Defaults” to reset BIOS settings.
- Disable any “Auto OC” or “Enhanced Turbo” features.
- Set the CPU ratio to “Auto” to eliminate manual overclocking.
- Save changes and reboot.
Turn Off CPU Boost Technologies:
Disable Intel Turbo Boost or AMD Precision Boost in the BIOS if you prefer manual control over overclocking.
Update BIOS, Chipset, and Utility Drivers:
Ensure all firmware and driver updates are installed to address potential conflicts and inaccuracies in reported CPU speeds.
Check CPU Cooler Mount and Clean Fans:
Re-seat the CPU cooler to eliminate potential thermal throttling.
Clean accumulated dust from CPU cooler and case fans to optimize cooling efficiency.
Replace Defective Hardware:
If other measures fail, consider replacing potentially faulty components such as the PSU or motherboard.
Read More: Can Cinebench Damage CPU | Best Practices In 2023
Signs Of An Overclocked CPU And Additional Considerations:
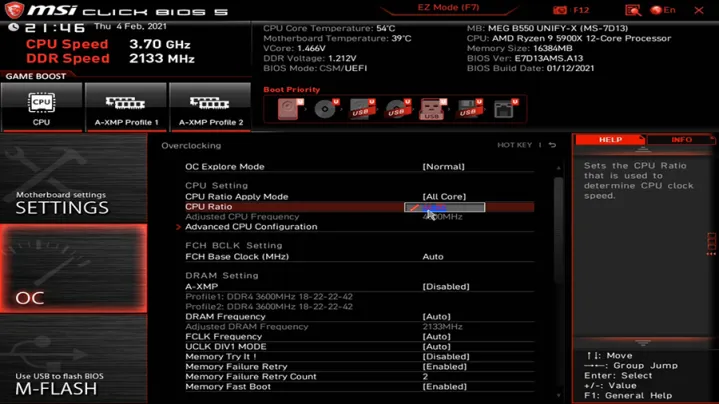
Besides observing clock speeds, be vigilant for signs indicating potential overclocking, including overheating; system freezes, WHEA errors in the Windows Event Viewer, and failed stress tests.
- Sudden power surges or spikes can disrupt CPU operations, causing erratic clock speeds. Use a surge protector for protection.
- Built-up static electricity discharging onto the motherboard may corrupt CPU operations and lead to unpredictable clock speeds. Ground yourself when working on PC internals.
- Malicious software, such as viruses and trojans, could manipulate the CPU, causing it to exhibit unstable clock speeds. Run antivirus scans to detect and remove infections.
- Active Windows power plans may force the CPU to operate constantly at maximum speed, leading to erratic clock speeds. Check and optimize power plan settings.
- Incorrectly configured voltage settings in BIOS could overdrive the CPU, resulting in abnormal clock speeds. Reset BIOS to eliminate bad profiles.
Monitoring And Stress Testing Tools:
Use monitoring utilities like Task Manager, HWiNFO, Core Temp, CPU-Z, AMD Ryzen Master (for AMD CPUs), and Intel Extreme Tuning Utility (for Intel CPUs) to keep track of CPU clock speeds. Stress testing tools such as Prime95, AIDA64, and OCCT can help validate the stability of an overclocked CPU.
Alternatives To Traditional Overclocking:
For users wary of traditional overclocking risks, consider alternative methods for improving performance:
- RAM Overclocking: Increase RAM speed through XMP profiles.
- Undervolting: Lower CPU voltage for higher turbo boost speeds with reduced power and heat.
- Windows Optimization: Disable unnecessary background processes and optimize Windows settings for improved performance.
Read More: B550 Gaming Plus CPU Light On – Causes & How To Fix In 2023
Frequently Asked Questions:
1. Can A CPU Overclock Automatically?
Depending on the motherboard, the BIOS might have an Automatic Overclocking or OC Level function, providing a safe overclocking boost.
2. Is It OK To Not Overclock The CPU?
While not necessary, overclocking can enhance performance. However, extreme overclocking can reduce lifespan, stability and void warranties.
3. Can Overclocking The CPU Damage The Motherboard?
Yes, overclocking a CPU can damage the motherboard. If the CPU is overclocked excessively, it can generate higher heat levels and draw more power, which may stress the motherboard’s components and lead to damage over time.
4. What Are The Dangers Of Overclocking?
Overclocking raises power consumption and heat, leading to crashes, freezes, or permanent damage. Monitoring temperatures and voltages is crucial.
5. How Much CPU Overclocking Is Safe?
There’s no universal limit; each CPU varies. Typically, marginal improvements of 100Hz- to 300Hz improvements are safe for daily use with proper cooling.
Conclusion:
Overclocking a CPU is a complicated topic, and it’s essential to know why your system overclocks itself to keep it stable and reliable. By following the steps in this guide, users can carefully find and fix problems caused by CPU overclocking that weren’t meant to happen. A careful method will help make sure your CPU works at its intended speeds without any sudden changes, whether you’re changing the BIOS settings, updating drivers, or fixing hardware issues.
Read more:
