How To Heat Up CPU? – A Comprehensive Ways and Tips
Heating a CPU intentionally is not a common practice, but there are instances where users might find it necessary. This is often done for stress testing or overclocking to push the processor beyond normal limits.
While not recommended for stress testing or overclocking, run CPU-intensive programs, overclock cautiously, use stress testing software, reduce cooling efficiency, disable throttling features, and increase ambient temperature.
In this article, we’ll explore various ways to intentionally heat up your CPU, the potential dangers of doing so, and provide tips for a controlled and safe process.
Ways To Heat Your CPU:

1. Run CPU-Intensive Programs:
Execute applications that put a heavy load on your CPU. Video editing software, data compression tools, 3D rendering programs, and multi-threaded applications are examples of software that can stress your CPU.
2. Overclock the CPU:
Overclocking involves adjusting your CPU’s clock speed and voltage settings to make it operate at higher frequencies than the manufacturer’s specifications. This can increase the heat generated by the CPU.
3. Use Stress Testing Software:
Employ stress testing tools designed to push your CPU to its limits. Programs like Prime95, AIDA64, or Intel Burn Test are commonly used for stress testing. These applications simulate demanding workloads to evaluate system stability under extreme conditions.
4. Reduce Cooling Efficiency:
Limit the efficiency of your cooling system intentionally. This could involve blocking the computer case’s airflow, obstructing the CPU fan, or using a smaller heatsink than recommended.
Be cautious when employing this method, as it can lead to excessive temperatures and potential damage.
5. Disable Throttling Features:
Throttling features such as SpeedStep, Turbo Boost, and power-saving modes are designed to reduce CPU performance and heat generation during periods of low demand.
Disabling these features can result in a higher, sustained level of CPU activity and increased temperatures.
6. Increase Ambient Temperature:
Manipulate the environment around your computer to raise the overall ambient temperature. You can achieve this by using a space heater or placing the computer in a warmer room.
Read: CPU Machine Check Architecture Error Dump – Fixed In 2023
Dangers Of Overheating Of CPU:

1. Hardware Degradation:
Excessive heat can cause permanent damage to the internal components of the CPU. Over time, prolonged exposure to high temperatures may lead to the degradation of the semiconductor materials, affecting the processor’s performance and lifespan.
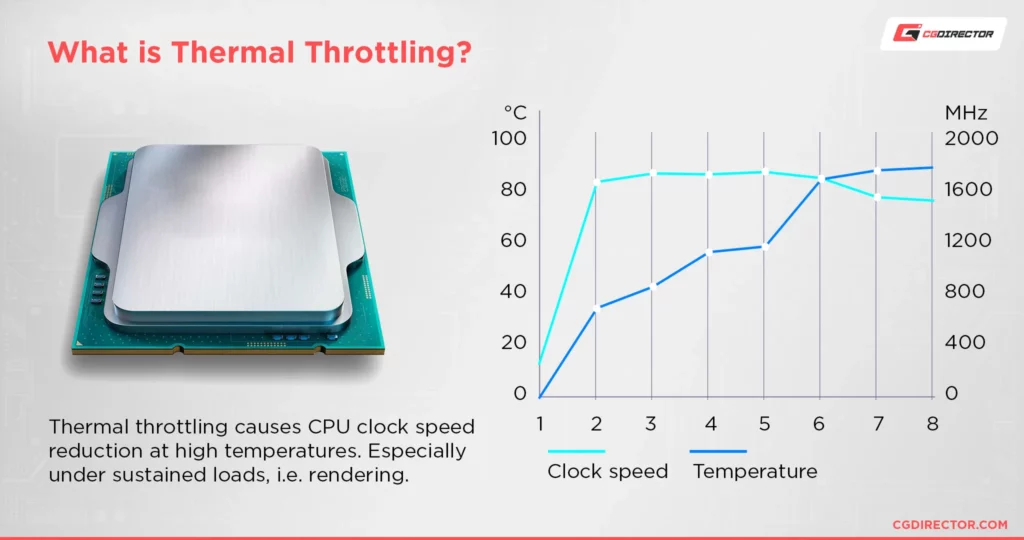
2. Thermal Throttling:
To prevent overheating, CPUs are equipped with built-in safety mechanisms, such as thermal throttling. When temperatures reach critical levels, the CPU may automatically reduce its clock speed and performance to lower the heat output.
While this protects the CPU from immediate damage, it can decrease system performance.
3. Emergency Shutdowns:
In extreme cases of overheating, modern computers have safety measures in place to shut down the system automatically.
This emergency shutdown prevents further damage but can result in the loss of unsaved data and potential file corruption.
4. Instability And Crashes:
Overheating can lead to system instability. As the CPU temperature rises, it may cause the computer to become increasingly unstable, resulting in frequent crashes, freezes, and unexpected shutdowns.
5. Data Loss:
Uncontrolled overheating can contribute to data loss. Sudden shutdowns or crashes due to high temperatures may interrupt ongoing processes, leading to file corruption or data loss, especially if files were being actively written or edited.
6. Reduced Component Lifespan:
High temperatures can significantly reduce the overall lifespan of computer components, including the CPU.
Frequent exposure to elevated temperatures accelerates wear and tear on the internal components, potentially shortening their operational lifespan.
7. Damage to Surrounding Components:
Excessive heat doesn’t only affect the CPU; it can also impact other components nearby. Motherboards, RAM modules, and graphics cards may experience adverse effects from prolonged exposure to high temperatures.
8. Difficulty in System Diagnosis:
Overheating issues can sometimes be challenging to diagnose because the symptoms—such as system crashes and instability—may be attributed to various factors. Identifying and resolving the root cause of overheating requires careful troubleshooting.
Read: Fatal Glibc Error: CPU Does Not Support X86-64-V2 – Fixing Error 2023
Tips For Safe Heating Up CPU:
1. Monitor Temperatures Carefully:
Use reliable temperature monitoring software to monitor your CPU temperatures closely. Regularly check the readings during the heating process to ensure they stay within safe limits.
2. Stress Test Gradually And Briefly:
When engaging in stress testing or any activity that intentionally increases CPU load, do so gradually and for short durations. This allows you to assess the impact on temperatures without exposing your CPU to extended periods of high stress.
3. Use a Good Cooling System:
Ensure that your computer is equipped with a high-quality cooling system. This includes an efficient CPU cooler, proper ventilation, and adequate airflow within the computer case. Investing in a reliable cooling solution is essential for managing increased heat.
4. Enable Safety Shut-Off Features:
Keep safety features enabled in your BIOS settings. These features, such as automatic shutdowns and thermal throttling, are designed to protect your CPU from reaching dangerous temperatures. Enabling them ensures that your system takes corrective action if temperatures become too high.
5. Avoid Prolonged Exposure To High Temperatures:
Intentional heating should be a controlled and temporary process. Avoid prolonged exposure to high temperatures, as this can lead to long-term damage and reduce the overall lifespan of your CPU.
Read: CPU DXE Initialization Is Started – How To Fix In 2023
Alternative Options For Heating CPU:

1. Upgrade To A Better CPU Cooler:
Investing in a more efficient CPU cooler is one of the most effective ways to manage temperatures during intensive tasks and overclocking.
Upgrading to a high-quality air or liquid cooling solution can provide better heat dissipation and help maintain a cooler operating temperature for your CPU.
Consider coolers with larger heat sinks, improved fan designs, or advanced liquid cooling systems for enhanced thermal performance.
2. Improve Case Airflow:
Optimize your computer case airflow for efficient cooling by strategically placing fans and eliminating obstructions.
Ensure a balanced intake and exhaust configuration, manage cables neatly, and regularly clean dust.
This enhances heat dissipation, promoting a cooler environment to safeguard your components during demanding tasks or overclocking.
Read: Normal CPU Temp While Watching Youtube – CPU Temp Guidelines
Frequently Asked Questions:
1. How Long Does The CPU Take To Heat Up?
The time it takes for a CPU to heat up can vary based on workload, cooling efficiency, and the specific processor model. In general, CPUs can heat up almost instantly under heavy workloads, especially if the workload is demanding.
2. What Causes CPU Temp To Rise?
Several factors can cause CPU temperatures to rise, with dust accumulation significantly contributing. Dust and dirt obstruct fans, vents, and heatsinks, impeding proper airflow and cooling.
3. Is 80 Degrees OK For The CPU?
While CPUs can tolerate temperatures up to a certain extent, 80 degrees Celsius (176°F) is considered higher. Ideally, keeping CPU temperatures lower is better to ensure optimal performance and longevity.
Conclusion:
While intentionally heating your CPU can be done for specific purposes, it’s crucial to approach it with caution.
Be aware of the potential risks and implement safety measures to prevent hardware damage. Remember that sustained high temperatures can harm your CPU’s lifespan and performance.
Always prioritize safe practices and consider alternative options, such as upgrading your cooling system, to achieve optimal performance without compromising the integrity of your hardware.
