CPU Overheating Alert MSI | How To Fix CPU Overheating?
MSI motherboards are renowned for their performance. One crucial feature that sets MSI motherboards apart is their CPU overheating alert system, which is pivotal in safeguarding your system from overheating and potential damage.
To fix the CPU Overheating Alert on MSI motherboards, check your CPU cooler, ensure proper airflow, clean your system, and reapply thermal paste if necessary.
This article will delve into MSI’s CPU overheating alert system, explain its solutions, and how to use it effectively to ensure your CPU remains within safe temperature limits.
How To Fix CPU Overheating Alert On MSI?
1. Cooling System Inspection:
It’s essential to verify that the AIO cooler is functioning correctly. One tube is warm while the other is cool, indicating a potential issue with the AIO’s pump or coolant flow. A properly working AIO should have both tubes at a similar temperature.
Ensure your Noctua NH-U12S SE cooler is installed correctly. Double-check that the cooler is securely and evenly mounted on the CPU. If you have doubts about the AIO’s performance, replacing it with a new one might be worthwhile.
2. Thermal Paste Reapplication:
It would help to reapply the thermal paste, which is an excellent step to ensure proper thermal conductivity between the CPU and cooler. Ensure the thermal paste application is correct and the cooler is securely mounted to the CPU.
3. Check The Heat Sink:
Ensuring that the heat sink is appropriately connected to the CPU is crucial. Even a slightly loose connection can compromise cooling efficiency. Make sure it’s firmly seated and that thermal paste, if used, is correctly applied.
- Power off your computer and unplug it.
- Carefully unscrew the computer case and expose the motherboard.
- Locate the heat sink connected to your CPU.
- Confirm that the heat sink is correctly positioned and securely attached to the CPU.
- If necessary, reseat the heat sink and reapply the thermal paste for optimal heat transfer.
4. Check For BIOS Updates:
It would be best if you were reluctant to update the BIOS; it’s worth considering this as a potential solution. BIOS updates often include improvements to system stability, including temperature management.
5. Check For Proper Fan And Pump Operation:
Verify that the fans on the radiator are working correctly and that the pump is operational. If you notice any irregularities or unusual noises, it could indicate a hardware problem.
6. Case Airflow:
Ensure that your PC case has adequate airflow. Good airflow can significantly impact CPU temperatures. Ensure that there are no obstructions in the airflow path and that your case fans work efficiently.
6. Fan Speeds:
Check if the cooler’s fans are spinning correctly. Ensure that they are running at an appropriate speed. You can adjust fan speeds in the BIOS or use software like MSI Afterburner to monitor and control fan speeds.
7. GPU Position:
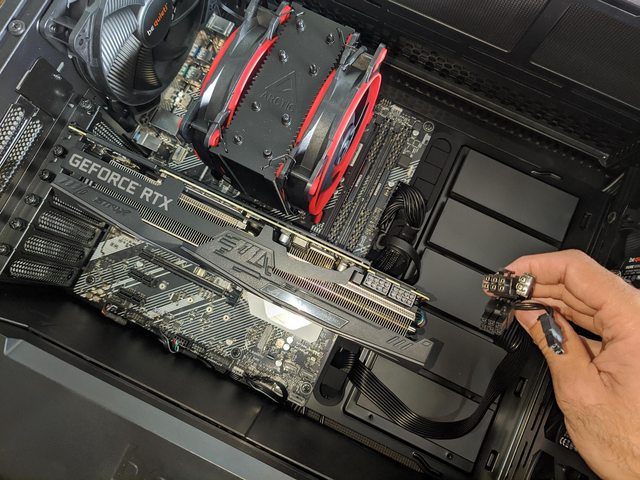

High-end GPUs can generate a lot of heat. Ensure the GPU isn’t too close to the CPU cooler, which might heat the air around the CPU. Try to maintain some space between the GPU and CPU cooler.
8. Stop Overclocking:
Overclocking can indeed increase CPU temperatures significantly. If you’ve overclocked your CPU, returning it to its default settings can help reduce heat output. Remember that overclocking should be done with caution and while monitoring temperatures closely.
- Access your computer’s BIOS or UEFI settings.
- Disable any overclocking settings or profiles.
- Save the changes and exit the BIOS/UEFI.
- Monitor the temperature to see if the issue persists.
10. Monitoring:
Use software like HWiNFO or MSI Afterburner to monitor your gaming CPU and GPU temperatures. This will help you pinpoint when and where the overheating occurs.
11. Undervolting/Power Limiting:
Ryzen CPUs can sometimes benefit from undervolt or power limiting. These techniques can reduce heat generation and power consumption while maintaining good performance. You can experiment with Ryzen Master or BIOS settings to achieve this.
12. Consider Upgrading Cooling:
If your CPU temperatures are still higher than desired, consider upgrading to a larger AIO or high-end air cooler. A 240mm or 360mm AIO cooler would provide more cooling capacity.
If you continue to experience overheating issues, consider upgrading your CPU cooler to a more robust model, especially if you plan to run your Ryzen 9 5900X at high loads frequently.
14. Clean Your System:
Dust accumulation is a common cause of overheating. Dust can clog up fans and heatsinks, reducing their ability to dissipate heat. Regular PC cleaning, including the CPU cooler and other components, is essential for optimal cooling. Compressed air can be used to blow away dust effectively.
- Power off and unplug your computer.
- Carefully open the case to access internal components.
- Remove dust from fans, heatsinks, and other components using compressed air.
- Clean the CPU cooler and ensure that airflow paths are unobstructed.
- Reassemble your computer and ensure proper cable management for airflow.
How To Use MSI’s CPU Overheating Alert System?
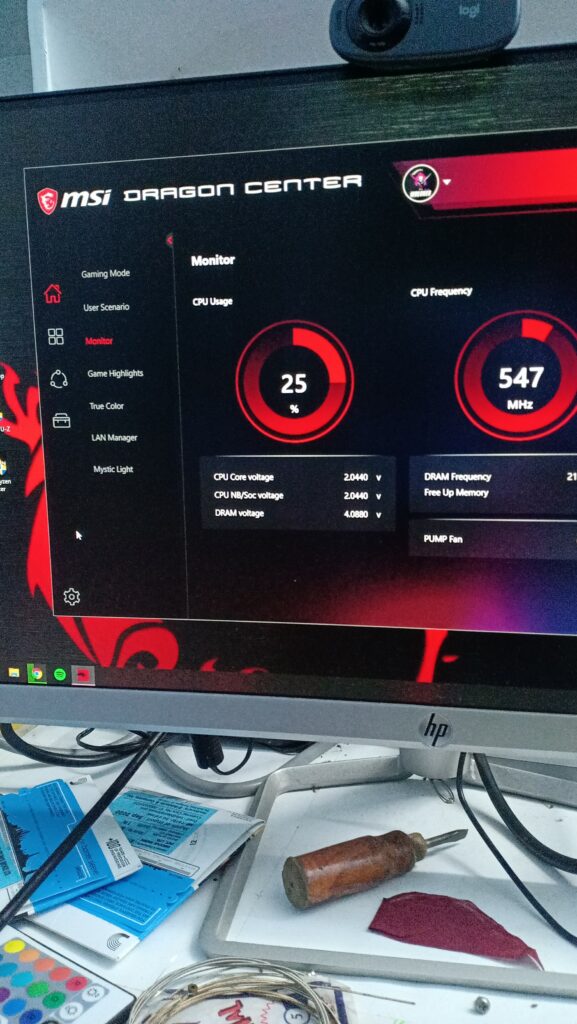
Setting up and using MSI’s CPU overheating alert system is relatively straightforward:
- Download and install MSI Dragon Center from MSI’s official website if it is not pre-installed on your system.
- Open the Dragon Center software and navigate to the “Hardware Monitor” or similar section, depending on your motherboard model.
- Set your desired CPU temperature thresholds and select your preferred alert method (pop-up notification, email, or mobile notification).
- Keep the Dragon Center application running in the background while using your computer. It will continuously monitor the CPU temperature.
- Take immediate action if an alert is triggered due to overheating. This could involve closing resource-intensive applications, increasing fan speeds, or checking for dust and debris in your computer’s cooling system.
FAQs:
1. What Are The Risks Of Ignoring CPU Overheating Alerts?
Ignoring CPU Overheating Alerts can damage your CPU and other system components for a long time. Prolonged overheating can cause instability, reduced CPU lifespan, and potential data loss.
2. Can I Adjust The CPU Temperature Threshold For The Overheating Alert On MSI Motherboards?
Yes, many MSI motherboards allow you to customize the CPU temperature threshold for the Overheating Alert in the BIOS settings. Check your motherboard’s manual for instructions on how to do this.
3. Why Is My CPU Overheating For No Reason?
Dust accumulation on fans or air vents is the primary culprit behind computer overheating. Minimizing heat buildup within the computer is essential to enhance system performance and safeguard internal components from harm.
4. How Do I Know If My CPU Is Damaged From Overheating?
The system boots up but shuts down automatically after a short period. The reported CPU operating frequency is less than expected. Evidence of CPU throttling. General slowness of the system.
5. Can A Failing Power Supply Unit (PSU) Cause CPU Overheating Alerts?
Yes, a failing or underpowered PSU may not provide sufficient voltage to components, leading to overheating issues. Ensure your PSU is in good condition and provides adequate power for your system.
6. Is It Safe To Continue Using My Computer When CPU Overheating Alerts Occur?
It’s not advisable to continue using your computer when CPU Overheating Alerts appear. Prolonged exposure to high temperatures can damage your CPU and other components. Shut down your system, investigate the issue, and address it before using your computer again.
Conclusion:
CPU overheating is a common issue that can be addressed with proper troubleshooting and maintenance. By following the solutions and tips outlined in this article, you can help prevent CPU overheating, maintain system stability, and prolong the lifespan of your computer components. Regular cleaning and monitoring ensure your CPU operates at optimal temperatures, enhancing your computing experience.
Sources:
- https://forum-en.msi.com/index.php?threads/cpu-overheating-when-starting-windows.376206/
- https://forums.tomshardware.com/threads/solved-hopefully-cpu-overheating.3736385/
- https://www.minitool.com/news/cpu-over-temperature-error-017.html
- https://community.amd.com/t5/processors/ryzen-5-3600-overheating-warning-during-restart/td-p/442202
